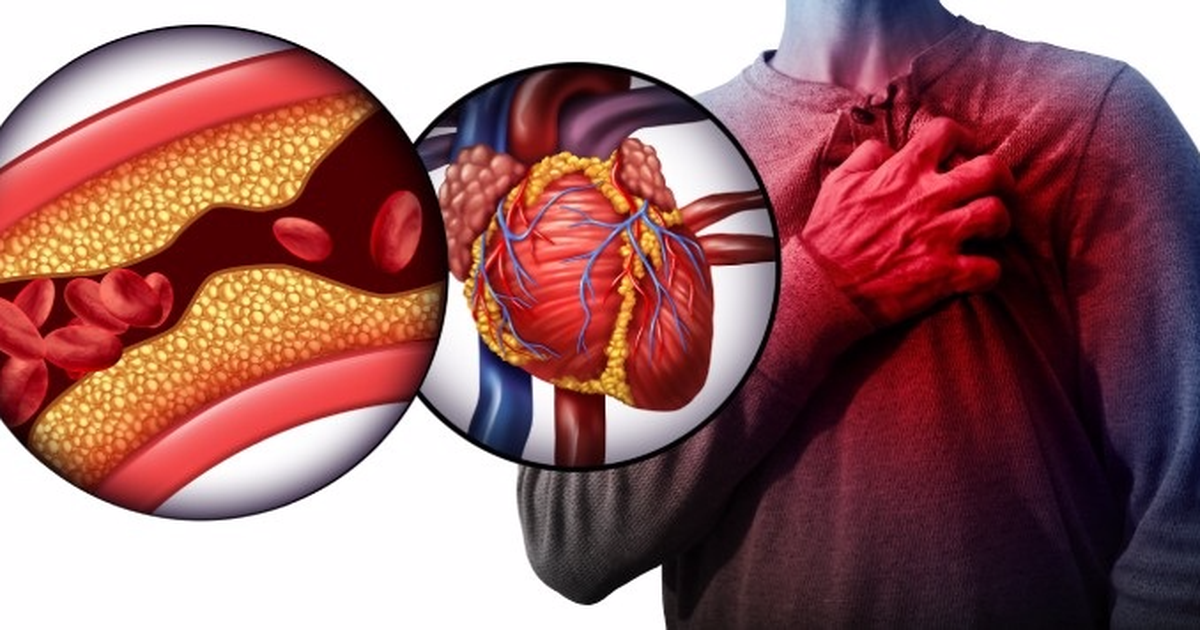
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is currently the leading cause of death worldwide and an increasing health burden in Vietnam. Population aging along with classical cardiovascular risk factors are the main causes of CAD.
However, rapid lifestyle changes and urbanization have led to a continuous increase and noticeable younger onset of this disease.
“Each week, Nguyen Trai Hospital admits a significant number of myocardial infarction cases, including about 1-2 cases among very young individuals, some even just over 20, completely healthy, with no underlying conditions.
Previously, this disease was considered an ‘elderly person’s disease’. However, recent cases are the clearest evidence that coronary artery disease is no longer exclusive to older adults,” shared TS.BS Nguyen Van Si, Deputy Head of Cardiology Department 1, Nguyen Trai Hospital, and senior lecturer at Ho Chi Minh City University of Medicine and Pharmacy, with Dân trí on the sidelines of the recent International Cardiology Conference organized by Nguyen Trai Hospital.
Dr. Hung reporting at the conference (Photo: DL).
Dangerous Disease Attacking Young People
Coronary artery disease is a condition where atherosclerosis occurs in the arteries supplying the heart. With over 20.5 million deaths annually, it is the leading cause of death worldwide.
In patients with CAD, when an atherosclerotic plaque ruptures suddenly, a blood clot forms within minutes, completely blocking an important coronary artery branch, causing a myocardial infarction (heart attack). This can lead to cardiac arrest and immediate death. This is also the most common cause of sudden death today.
According to Dr. Si, just 10-15 years ago, CAD was typically found in people over 50. Today, the average age has dropped to under 40, sometimes even under 30.
This trend of the disease affecting younger people primarily stems from modern lifestyles with prolonged work pressure and sedentary habits leading to overweight and obesity. Eating habits rich in bad fats and sugar, smoking, and alcohol consumption also cause plaques to form earlier.
At the same time, many studies also show that East Asians and Southeast Asians tend to carry genes that promote atherosclerotic plaque formation, leading to CAD. This explains some cases where individuals are diagnosed with heart disease despite having a balanced physique and healthy lifestyle.
What to Do if You Carry Genes for Cardiovascular Disease?
Dr. Si examining and consulting with a patient (Photo: BV).
According to TS.BS Nguyen Van Si, to prevent cardiovascular disease, people need to limit stimulants (alcohol, beer, tobacco), exercise at least 30 minutes/day, eat healthily, limit fried foods, soft drinks, fast food, maintain a healthy weight, control blood pressure, blood sugar, blood lipids, reduce stress, and get enough sleep.
For individuals with high genetic risk, this needs special attention. Currently, medical science offers genetic risk assessment tests based on polygenic risk scores for CAD prevention.
According to the doctor, one of the newest and most important points in current prevention strategies is considering genetic factors. Although genes are unchangeable, knowing the genetic risk early serves as motivation to control other modifiable cardiovascular risk factors.
“The importance of genetic risk assessment is to inform patients early of their risk, thereby allowing them to adjust their lifestyle and avoid cumulative disease-causing factors,” Dr. Si emphasized.
In addition to the recommendations above, patients need strict regular screening. When any risk factors appear (hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, etc.), everyone needs early treatment to reach targets and frequent monitoring.
People should also pay special attention to the signs of acute myocardial infarction, which include severe chest pain lasting more than 15 minutes and not subsiding with rest. This is a warning sign that requires immediate hospitalization for timely diagnosis, increasing the chance of survival.